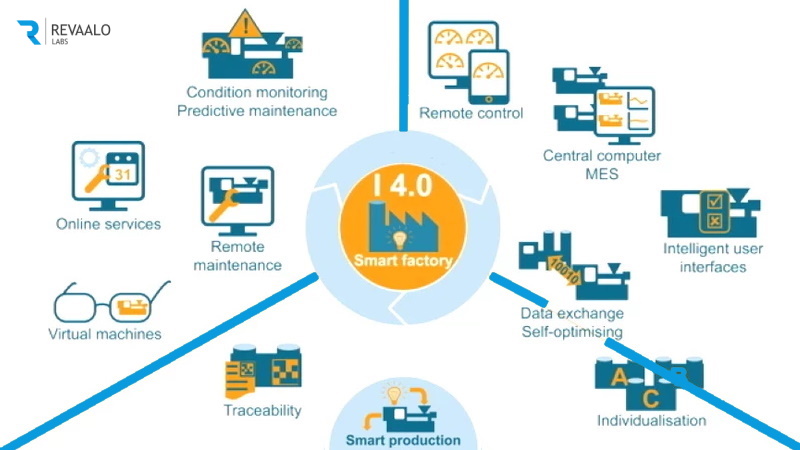
What is a Smart Factory?
The term “smart factory” gets thrown around a lot these days, but what does it actually mean? At its core, a smart factory is a manufacturing environment that leverages technology to optimize every aspect of the production process. This isn’t just about robots; it’s a holistic approach integrating data analytics, automation, artificial intelligence (AI), and the Internet of Things (IoT) to create a highly efficient and responsive system. Think of it as a manufacturing facility on steroids, powered by smart technology that makes it faster, more flexible, and more resilient than traditional models.
The Role of Data Analytics in Smart Factories
Data is the lifeblood of a smart factory. Sensors embedded in machines, robots, and even products themselves collect vast amounts of information about the production process – everything from machine performance and energy consumption to product quality and inventory levels. Advanced analytics tools then sift through this data, identifying trends, predicting potential problems, and optimizing production parameters in real time. This allows for proactive maintenance, preventing costly downtime and improving overall efficiency. Imagine being able to predict a machine failure days before it happens, giving you ample time to schedule repairs and avoid production disruptions.

Automation: The Backbone of Smart Manufacturing
Automation is another crucial component of smart factories. While traditional factories might employ automated systems for specific tasks, smart factories take automation to a whole new level. Robots and automated guided vehicles (AGVs) handle a wider range of tasks, working alongside human employees to improve efficiency and reduce human error. This isn’t about replacing human workers entirely; it’s about empowering them to focus on more complex and creative tasks, freeing them from repetitive or dangerous jobs. This collaboration between humans and machines is key to the success of smart factories.
The Power of Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI is quickly becoming a game-changer in smart manufacturing. Machine learning algorithms analyze vast datasets to identify patterns and make predictions, enabling more accurate forecasting, optimized scheduling, and improved quality control. AI-powered systems can also learn from past performance, constantly adapting and improving their efficiency. This self-learning capability allows smart factories to continuously optimize their operations, becoming more efficient and responsive over time. From predictive maintenance to real-time quality control, AI plays a crucial role in making smart factories truly smart.
The Internet of Things (IoT) and Connectivity
The Internet of Things (IoT) is the glue that holds a smart factory together. By connecting all the different components of the manufacturing process – machines, sensors, robots, and even the products themselves – to a network, smart factories can achieve seamless data flow and real-time visibility. This interconnectedness allows for better coordination, improved communication, and faster decision-making. Imagine a scenario where a sensor detects a problem on the production line; the IoT network immediately alerts the relevant personnel, allowing for a quick response and minimizing production downtime.
Smart Factories and the Workforce of the Future
The transition to smart factories requires a skilled workforce capable of operating and maintaining advanced technologies. This means investing in training and development programs to equip employees with the skills they need to succeed in this new environment. Smart factories demand a workforce that is comfortable working alongside robots, analyzing data, and utilizing advanced software. The focus shifts from repetitive manual labor to higher-level tasks involving problem-solving, critical thinking, and collaboration.
Challenges and Opportunities
While the potential benefits of smart factories are enormous, there are also challenges to overcome. The initial investment in technology can be substantial, and there can be challenges in integrating different systems and data sources. Data security is also a major concern, as smart factories generate and process a vast amount of sensitive data. However, the long-term benefits – improved efficiency, reduced costs, and increased competitiveness – far outweigh the challenges. Smart factories represent a significant opportunity for manufacturers to enhance their productivity and remain competitive in a rapidly evolving global market.
The Future is Smart
Smart factories are not just a futuristic concept; they are already a reality for many manufacturers worldwide. As technology continues to advance, we can expect even greater levels of automation, intelligence, and connectivity in the years to come. The adoption of smart factory technologies will be crucial for manufacturers seeking to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance their competitiveness in the global marketplace. The future of manufacturing is here, and it’s smart. Read also about smart factory examples.
