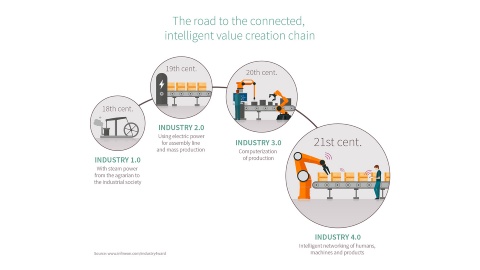
The Rise of the Connected Factory
Smart factories are no longer a futuristic fantasy; they’re rapidly becoming the reality of modern manufacturing. This shift is driven by the convergence of several powerful technological advancements, including the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), big data analytics, and cloud computing. These technologies are interwoven to create a highly interconnected and automated production environment, where machines communicate with each other, data flows seamlessly, and processes are optimized in real-time. This interconnectedness allows for a level of efficiency and responsiveness previously unimaginable.
Data-Driven Decision Making: The Heart of the Smart Factory
At the core of every smart factory is a robust data infrastructure. Sensors embedded in machinery and throughout the production process collect vast amounts of real-time data – everything from machine performance and energy consumption to product quality and supply chain logistics. This data is then analyzed using sophisticated AI algorithms to identify trends, predict potential problems, and optimize production processes. This predictive capability allows manufacturers to proactively address issues before they escalate, minimizing downtime and maximizing output. The insights gleaned from this data are invaluable for making informed decisions across the entire organization.
Automation and Robotics: Enhancing Efficiency and Productivity
Automation and robotics are crucial components of the smart factory revolution. Robots are no longer simply performing repetitive tasks; they’re collaborating with human workers, handling complex operations, and adapting to changing conditions. Advanced robotics, guided by AI and machine learning, can perform tasks with greater precision, speed, and consistency than human workers, leading to significant improvements in productivity and product quality. This automation frees up human workers to focus on more strategic and creative tasks, fostering a more collaborative and efficient work environment.
The Internet of Things (IoT): Connecting the Factory Floor
The IoT is the nervous system of the smart factory, linking all machines, sensors, and devices into a unified network. This connectivity enables real-time monitoring of the entire production process, from raw material delivery to finished product shipment. The data generated by IoT devices provides a comprehensive overview of factory operations, allowing managers to identify bottlenecks, optimize workflows, and ensure smooth and efficient production. The seamless flow of information facilitates better communication and collaboration between different departments and stakeholders.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning: Driving Intelligent Automation
AI and machine learning are transforming the way smart factories operate. These technologies are used to analyze vast amounts of data, identify patterns, and predict future outcomes. This predictive capability allows for proactive maintenance, preventing equipment failures and minimizing downtime. AI-powered systems can also optimize production schedules, manage inventory levels, and improve product quality. The ability of AI to learn and adapt over time allows for continuous improvement and optimization of factory processes.
Cybersecurity: Protecting the Connected Factory
With the increased connectivity of smart factories comes the increased risk of cyberattacks. Protecting the sensitive data and critical infrastructure of a smart factory is paramount. Robust cybersecurity measures are essential to prevent unauthorized access, data breaches, and disruptions to production. This includes implementing strong network security, employing advanced threat detection systems, and regularly updating software and firmware. A comprehensive cybersecurity strategy is not just a matter of compliance; it’s crucial for the continued operation and success of the smart factory.
The Human Element: Collaboration Between Humans and Machines
Despite the increasing automation in smart factories, the human element remains vital. Smart factories are not about replacing humans with machines; they’re about creating a collaborative environment where humans and machines work together to achieve greater efficiency and productivity. Human workers are still needed for tasks requiring creativity, problem-solving, and critical thinking. The focus is on upskilling the workforce to manage and maintain advanced technologies, ensuring a smooth transition to the smart factory model and maximizing the benefits of this technological advancement. Investing in training and development programs is essential for a successful integration of human capital within the smart factory environment.
Sustainability and the Smart Factory
Smart factories are not only about increasing efficiency and productivity; they also offer significant opportunities for improving sustainability. By optimizing energy consumption, reducing waste, and improving resource utilization, smart factories can contribute to a more environmentally friendly manufacturing process. Data analytics can help identify areas for improvement in energy efficiency, and automation can minimize waste and reduce material consumption. The integration of renewable energy sources and the implementation of circular economy principles further enhance the sustainability efforts of smart factories, leading to a more responsible and environmentally conscious approach to manufacturing. Please click here to learn about the definition of smart factories.
